President Recep Tayyip Erdogan said Saturday that Turkey aims to reduce its dependence on foreign energy sources.
Speaking at a campaign rally for local March 31 elections in northwestern Edirne province, Erdogan said that Turkey aims to maximize domestic resource utilization in energy.
"In 2017, our electricity generation from domestic sources was 45 percent. Now, it has reached 60 percent," Erdogan said.
He also recalled that Turkey discovered new gas fields in Thrace with a reserve of 3 billion cubic meters that will double the country's current natural gas production.
"The production is enough to meet the consumption of 300,000 households for 10 years," he added.
Turkey has limited domestic energy resources and mainly depends on expensive energy imports for its consumption, which constitutes the biggest share of the current account deficit. The country strives to discover new oil and natural gas sources, and also heavily invests in renewable energy and domestic coal.
Source: AA

Turkey approved a 15.3 percent annual increase in public expenditure in its energy and mining sectors in 2019, the country's Official Gazette announced Monday.
Under the presidential decree for the government's 2019 investment program, the country will invest 9.81 billion Turkish liras for energy and mining projects this year, compared to 8.51 billion liras in 2018.
The country will allocate nearly 7.71 billion liras for 104 projects in the energy sector, and plans to budget approx. 2.10 billion liras for 49 projects in the mining sector.
Turkish Petroleum Pipeline Corporation (BOTAS) will have the lion's share of public investment in the energy sector. The country will allocate nearly 3.70 billion liras for the corporation's 15 ongoing and planned projects for 2019.
BOTAS will be followed by Turkish Electrical Transmission Company (TEIAS), which with its 31 projects this year will receive 1.99 billion liras.
Turkey’s State Hydraulic Works follows TEIAS as the third largest recipient will receive 1.12 billion liras for its 11 projects.
In the mining sector, the biggest share of public investment will be given to Turkish Petroleum with 1.26 billion liras for the company's 13 ongoing and planned projects in 2019.
The Mineral Research and Exploration General Directorate (MTA) will obtain 315.49 million liras for its 6 projects while Turkey's Electricity Generation Company (EUAS) will be allocated 168.26 million liras for its eight projects.
Source: AA

The Internet of Things (IoT) Security Institute (IoTSI) has released a framework to help governments, corporates and stakeholders in the smart city industry to address IoT security challenges.
The IoT security framework is specific to smart cities and critical infrastructure and is publicly available for implementation without licensing costs or additional charges.
Alan Mihalic president of the IoTSI says the objective is to provide frameworks that can be implemented from the base build through to the build completion.
The release is part of efforts to come up with a global standard for smart city and critical infrastructure security to help cities address factors including data confidentiality, privacy and public safety levels that meet community and corporate expectations in deploying IoT technologies.
“Buildings are working spaces, information portals and community information exchanges that require appropriate security controls to meet their future potential. The IoT Security Institute is focused on ensuring that recommendations produced are simple to adopt – fitting within existing processes wherever possible. To achieve this, the IoTSI opens the channels of communication between building occupiers, facilities managers, engineers, designers and urban planners in relation to the cyber security and privacy challenges affecting building environments.
“We did not want to restrict framework adoption by imposing licensing costs or restricted access pending some kind of commercial consideration. The framework is there to be implemented and shared. Often the benefits of such initiatives get lost in the commercial requirements imposed. The IoTSI does not even charge membership dues. We did not want to be caught up in forcing membership on order to participate. It too often drives many not- for-profit agendas. We simply and easily want to get the framework to cyber and privacy professionals where it is needed.
Source: Smart Energy International

Distribution system operators (DSOs) must substantially shift their responsibilities to enable the clean energy transition. Within the next decade, DSOs will undergo tremendous transformations to integrate massive volumes of renewables, deploy charging infrastructures for some 40 million electric vehicles and connect electric heat pumps, batteries and other grid edge technologies.
Such a high scale transformation requires substantial investments. Today, however, the EU support mechanism for the linking of energy infrastructure across borders is particularly focused on large transmission projects. Along the +170 financially supported projects, only 4 concern low voltage, smart grid initiatives. Yet, local and decentralised projects can bring positive effects to both national and regional levels, by easing congestion in cross-border regions and by integrating renewables.
In case the Trans-European Networks for Energy (TEN-E) Regulation would be revised as recently proposed by the European Parliament, Eurelectric together with CEDEC, EDSO and Geode – the four associations representing the DSOs at EU level – insist that the philosophy of the subsidising criteria must change to empower DSOs to play their central role for the energy transition.
Through a joint letter Eurlectric, CEDEC, EDSO and Geode call upon policymakers at EU and national level to ensure a more open-minded approach towards the definition of cross-border projects. This is crucial to ensure real benefits for prosumers and the deployment of effective new technologies.
Source: Eurelectric

Developers commissioned a little over 45GW of onshore wind turbines globally in 2018 compared with 47GW a year earlier. Just four manufacturers accounted for more than half, or 57%, of the machines deployed: Denmark’s Vestas, China’s Goldwind, GE Renewable Energy of the U.S. and Spain’s Siemens Gamesa.
The latest data from BloombergNEF (BNEF) show that Vestas extended its lead in the industry, with 10.1GW of its onshore turbines commissioned in 2018 – a global market share of 22% compared with 16% in 2017. The statistics draw on BNEF’s global database of wind projects and extensive information from the industry.
China’s Goldwind rose from third to second place, lifted by a strong performance in China, where it captured a third of the 19.3GW market. The company’s global footprint, however, remains limited: only 5% of Goldwind’s 6.7GW were commissioned outside China. GE came third with 5GW – six out of every ten GE turbines were commissioned in the U.S. Both GE and Vestas commissioned just over 3GW in the U.S., with Vestas leading by 44MW in the neck-to-neck race for U.S. market leadership.
Siemens Gamesa, formed in 2016 from a merger of the wind business of German engineering giant Siemens and the Spanish turbine maker Gamesa, dropped from second to fourth place, with 4.1GW commissioned in 2018. This is 40% less than in 2017, although the tally does not include a number of very large wind farms that are only partially built and will not come online until 2019.
“Chinese manufacturers rely almost solely on their home market,” said Tom Harries, senior wind analyst at BNEF and lead author of the BNEF report Global Wind Turbine Market Shares. “Of the European onshore wind turbine makers to make the top 10, Vestas and Nordex actually commissioned more capacity in the Americas than in Europe. Most of Enercon’s turbines are in Europe. Siemens Gamesa is the most diversified, with a near equal split across Europe, the Americas and Asia.”
“In offshore wind, it’s been a record year for China, and we will see more growth,” Harries continued. “Some 1.7GW of the global 4.3GW was commissioned there. In Europe it was a tight race between Siemens Gamesa and MHI Vestas. GE has some projects coming up in France, and we also expect to see orders for their new 12MW platform.”
Total onshore wind installations in 2018 were 11.7GW in the Americas, 8.5GW in Europe[1] and 1GW in Africa and the Middle East, while Asia accounted for 24.2GW. BNEF registered new wind farms starting full commercial operation in 53 countries.
David Hostert, head of wind research at BNEF, said: “Last year was a bit of a mixed picture in terms of global onshore wind installations, with only 45.4GW commissioned. Still, add to that 4.3GW offshore wind and 2018 ended slightly lower than 2017. Now it is time for the manufacturers to buckle up for two stormy years ahead: we predict demand for around 60GW of onshore capacity in both 2019 and 2020 with increases in all regions. However, a lot of this impressive-sounding volume rides on extremely competitive pricing, add-on products and services, and new financing models. This will be tough to deliver for the Big Four, let alone the smaller turbine makers.”
Source: BNEF

Oil and gas giant Royal Dutch Shell has agreed to buy 100 per cent of Sonnen, a German rival to Tesla and Samsung in providing homeowners with lithium-ion battery packs powered by solar energy.
Terms of the deal, announced on Friday, were not disclosed.
Sonnen, founded in 2010, has grown to become Europe’s largest maker of rechargeable energy storage packs.
It has installed more than 40,000 battery packs produced in its three factories in Germany, Australia and the US.
The German start-up previously received funding from GE Ventures, Envision Energy of China and Munich Venture Partners.
Shell first invested in Sonnen in May 2018 as part of its ‘New Energies’ project, which since 2016 has focused on the shift into alternative fuels for transport and power, including generating electricity, buying and selling it, and supplying it to customers. “Sonnen is one of the global leaders in smart, distributed energy storage systems and has a track record of customer-focused innovation. Full ownership of Sonnen will allow us to offer more choice to customers seeking reliable, affordable and cleaner energy,” said Mark Gainsborough, head of new New Energies at Shell.
Energy majors are preparing for a global shift towards cleaner fuels, forcing some of the biggest companies to reimagine their businesses.
European majors such as Shell, Total and Repsol have been making deals along the electricity supply chain — from power generation to vehicle charging and entering the world of household energy supply. Shell sees a future not only in gas for electricity generation but also in using the fuel as a back-up for renewable power.
Last year the company acquired UK power supplier First Utility giving it direct access to retail electricity consumers for the first time, and New Motion, one of Europe’s largest electric vehicle charging companies.
It said the deal sits well within its $2bn New Energies budget. The company plans to allocate 80 per cent of these funds into the power sector in the period to 2020. Still, this is a small proportion of its $25bn annual capital expenditure budget and Shell like its peers is grappling with how to deliver revenues from these new ventures that match those from its legacy oil and gas exploration and production businesses.
When Sonnen was launched, it sold battery power packs for €25,000 a unit. By 2017, the cost had plummeted to €5,000.
The start-up was founded by Christoph Ostermann, 48, a serial entrepreneur who has founded five companies since dropping out of high school. On Friday he described Shell as “the perfect partner” to help Sonnen expand into new markets. “Shell will help drive the growth of Sonnen to a new level and help speed up the transformation of the energy system,” he said.
Where Sonnen differs from Tesla and Samsung is through its various services. In 2015 it launched the “sonnenCommunity,” a virtual network to allow users — for a €20 monthly fee — to buy and sell excess energy to other members at reduced costs.
If the community does not use the power generated, Sonnen sells it back to the grid. Another offering, sonnenFlat, eliminated monthly fees altogether by turning homeowners’ batteries into a decentralised “virtual power plant,” taking in excess energy when needed, discharging it at other times, thereby performing a service to mitigate fluctuations in the power supply.
Shell and Sonnen said on Friday that the two companies will work together on “integrated energy services and electric vehicle charging solutions,” in addition to expanding Sonnen’s grid services.
Source: Financial Times
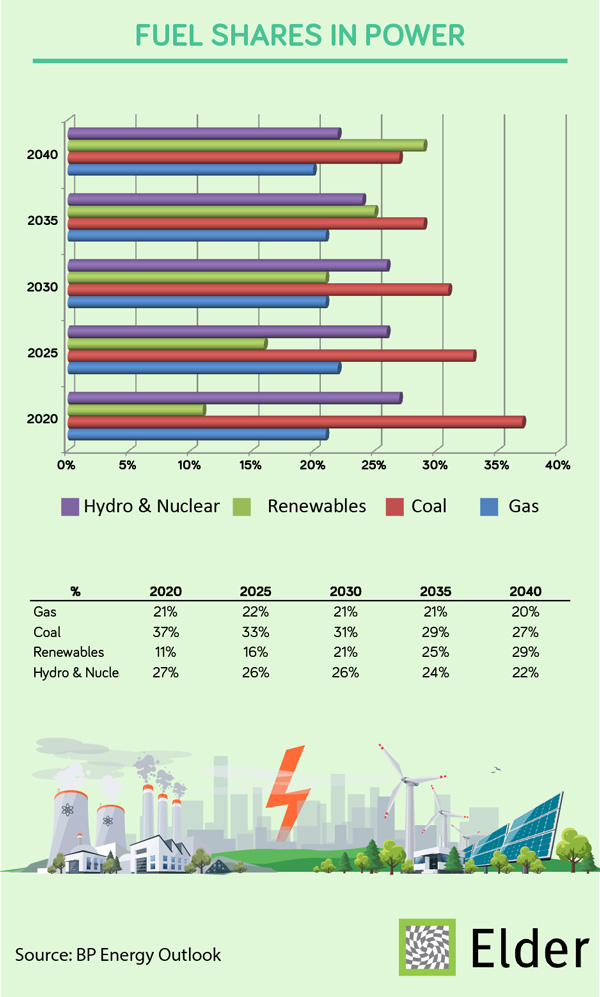
BP Energy Outlook
In all the scenarios considered, world GDP more than doubles by 2040 driven by increasing prosperity in fast-growing developing economies. In the Evolving transition (ET) scenario this improvement in living standards causes energy demand to increase by around a third over the Outlook, driven by India, China and Other Asia which together account for two-thirds of the increase.
Despite this increase in energy demand, around two-thirds of the world’s population in 2040 still live in countries where average energy consumption per head is relatively low, highlighting the need for ‘more energy’. Energy consumed within industry and buildings accounts for around three-quarters of the increase in energy demand. Growth in transport demand slows sharply relative to the past, as gains
in vehicle efficiency accelerate. The share of passenger vehicle kilometres powered by electricity increases to around 25% by 2040, supported by the growing importance of fully-autonomous cars and shared-mobility services.
Please click here to read the full report.