The trade volume of Turkey's day-ahead spot electricity market increased by 13% in July compared to the same month of 2019, according to data provided by Turkey's Energy Exchange Istanbul (EXIST).
The trade volume in the day-ahead spot electricity market, which EXIST started to operate in 2015, registered at about 4.9 billion liras this July compared to around 4.4 billion liras in July last year.
EXIST reported transactions in the day-ahead market in July of 16.6 million megawatt-hours.
The highest daily trade volume was recorded on July 29 at 184.6 million liras, while the lowest occurred on July 12 with 121.5 million liras.
The average electricity rate for one megawatt-hour in the day-ahead spot market in July was calculated as 296.36 liras.
Turkey's energy exchange company, responsible for operating energy trade, including power and gas commodities, provides counter-party guarantees in its transactions.
Source: Anadolu Agency

Turkey’s domestic manufacturing of thermal battery, a device that stores and releases high levels of electrical energy, has helped the country’s economy save $91 million (TL 630 million) since the start of its production in 2006, the technology minister said Tuesday.
Industry and Technology Minister Mustafa Varank said Ankara-based TUBITAK Defense Industries Research and Development Institute (SAGE), the sole national developer of thermal batteries (or thermopiles), has designed 250 models since it started the R&D project in 2002.
"Thirty-eight of these models have been in production and have been qualified with respect to globally accepted military standards," he said.
Thermal batteries are widely used as primary and secondary power sources in various military and aerospace applications, due to their reliable, maintenance-free and durable structure, as well as their capability of meeting long shelf-life requirements of more than 20 years. They are single-use (non-rechargeable) devices, custom-designed according to the system’s specifications. The batteries are supplied to Turkish defense companies such as ASELSAN, ROKETSAN and Turkish Armed Forces (TSK) for smart munitions systems. The product also acts as the main power supply to domestic missiles, including SOM cruise missile, HGK guidance kit, air to air missiles, the Gokdogan (Peregrine) and Bozdogan (Merlin).
Varank said SAGE has helped the country become self-sufficient to meet the entire domestic demand for thermal batteries and added that the country started to export the product since 2012. The minister said Turkey exports thermal batteries to different countries including Germany, Ukraine, Brazil and Saudi Arabia.
"The product has great export potential. We recently received a pre-order from another European Union country and are at the stage of signing an important contract," he added.
Source: Daily Sabah
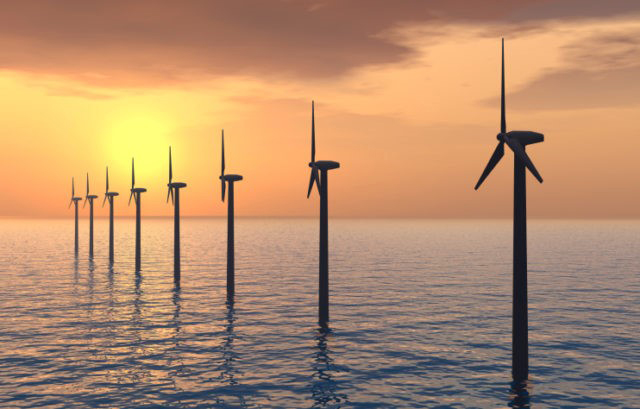

Global offshore wind capacity will surge to over 234 GW by 2030 from 29.1 GW at the end of 2019, led by exponential growth in the Asia-Pacific region and continued strong growth in Europe, according to a new report from the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC).
GWEC has today released the second edition of its Global Offshore Wind Report, which provides a comprehensive overview of the offshore wind sector globally with the latest data and analysis on market growth, industry forecasts to 2030 and data-based insights on emerging markets.
The report also includes lessons learnt on support schemes, industrial development and job creation, grid connection, cost reduction and supply chain, as well as health and safety to further drive growth of the global offshore wind market.
The report finds that 2019 was the best year on record for offshore wind, with 6.1 GW of new capacity added globally, bringing total global cumulative installations to 29.1 GW. China remains in the number one spot for the second year in a row for new installations, installing a record 2.4 GW, followed by the UK at 1.8 GW and Germany at 1.1 GW. While Europe continues to be the leading region for offshore wind, countries in the Asia-Pacific region, such as Taiwan, Vietnam, Japan, and South Korea, as well as the US market are quickly picking up the pace and will be regions of significant growth in the next decade.
GWEC Market Intelligence forecasts that through 2030, more than 205 GW of new offshore wind capacity will be added globally, including at least 6.2 GW of floating offshore wind. This represents a 15 GW increase from the forecasts in GWEC Market Intelligence’s pre-COVID forecast, demonstrating the resilience of the sector to play a major role in powering both the energy transition and a green recovery.
Ben Backwell, CEO at GWEC commented: “Offshore wind is truly going global, as governments around the world recognise the role that the technology can play in kickstarting post-COVID economic recovery through large-scale investment, creating jobs and bringing economic development to coastal communities.
Over the coming decade we will see emerging offshore markets like Japan, Korea and Vietnam move to full deployment, and see the first offshore turbines installed in a number of new countries in Asia, Latin America and Africa.
“The report shows that 900,000 jobs will be created in the offshore sector over the next decade – and this number can only increase if policymakers put in place recovery strategies that can further accelerate growth of the sector. Furthermore, 1 GW of offshore wind power avoids 3.5 MT CO2 – making it the most effective available large-scale technology to avoid carbon emissions and displace fossil fuels in many geographies”.
Source: Global Wind Energy Council

The European Commission has proposed to strengthen its 40% greenhouse gas emission reduction target to 50% or 55% on 1990 levels in the next ten years.
But this step does not meet the minimum level of ambition that climate science, and the EU’s own climate-neutrality goal, say is needed, writes Mirjam Wolfrum.
Setting its 2030 target at the right level will make a fundamental difference to our economy and society. The world’s climate science authority, the United Nation’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (UN IPCC), has said definitively that an extra 0.5°C of warming will be catastrophic. It could cost the global economy up to $15 trillion in additional climate impacts, add 10 cm to the rise in sea levels, and multiple by 10x the chance of an ice-free Arctic Ocean in summer.
But, with the European private sector showing more willingness to do more than the Commission’s proposal, the EU can set its ambition level higher and show global leadership to be in line with the latest science.
In a recent paper, the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) found that emissions must fall every year by 4.2% until 2030 to cap warming at 1.5°C.
Based on this insight, bringing the EU in line with the goal of the Paris agreement and its climate neutrality target would take at least a 55% drop in emissions – the upper limit of the Commission proposal.
This target is itself not ambitious enough to show global leadership. To put Europe’s 2030 target in line with the latest climate science – limiting warming to 1.5°C – would either call for a 60-65% 2030 target, or much more rapid reductions after 2030.
To deliver these cuts – and more – the European Commission should more proactively encourage more companies to set science-based targets (SBTs) for reducing emissions in line with this 1.5°C pathway.
Companies’ targets are science-based if they are in line with meeting the Paris agreement. The SBTi has approved the targets of over 200 European companies so far, who are therefore already contributing achieving the cuts needed for the Commission’s proposed 50% – 55% ambition.
If just these 200 targets are achieved, reductions in GHG emissions equivalent to 6% (250 MtCO2e) of the EU’s annual total will be delivered.
Some of Europe’s heaviest emitting companies are now onboard, with cement makers LafargeHolcim and HeidelbergCement, steelmaker thyssenKrupp and heavy truck business Scania all with approved SBTs.
This progress – more than double the number have been set in the past 18 months than the previous 3 years combined – shows the scale and possibility for Europe to increase policy ambition in this area, as the corporate sector is already there.
These companies’ actions will make or break whether the EU is to achieve its new goal. And they are showing the Commission’s current proposal is too light.
Over 70 companies in Europe, for example, already have targets which are more ambitious than the EU Commission’s proposal and in line with a maximum of 1.5°C of warming. That group includes some of Europe’s most successful businesses like Mercedes-Benz, Unilever, and AB InBev. This ambition level is equivalent to the EU agreeing a 60% to 65% 2030 target.
Europe’s big businesses are now showing greater willingness to lead, so EU leaders should ask more to catch up and leverage the private sector to deliver on its target faster.
With critical decisions on how the EU’s new €750 recovery plan will be spent now being discussed, the right policies to encourage more ambitious target-setting is key. According to a review by CDP and Oliver Wyman before the COVID-19 crisis, at least double the volume of annual low-carbon capital investment is needed by companies if the EU is to meet its climate-neutrality goal.
Among the current group of European companies with science-based targets, at least €11 billion will be spent on achieving them. The EU raising its 2030 target and asking more firms to set science-based targets, are the best ways for this investment gap to be filled.
Source: Euractiv

Britain’s first-ever polyphase SMETS2 smart meter was installed on Tuesday 4 August 2020 at a property in Gloucestershire, marking a significant milestone for the country’s transition to a smarter, greener energy system.
The device, installed by meter asset provider SMS plc for a customer of Good Energy, will provide homes and businesses connected to a three-phase electricity supply with the option of a smart meter. Three-phase power provides heavy loads of electricity and is predominantly used by industrial and commercial (I&C) or high-usage residential sites.
Designed by US-based smart infrastructure solutions provider, Aclara, the SGM1433-B (part of the SGM1430 polyphase family) is the first fully compliant and certified SMETS2 polyphase electricity meter for the UK market, and will deliver a solution for UK utilities to further automate the management of their meter assets at a total lower cost of ownership.
SMS has worked closely with Aclara and Smart DCC over the past 12 months in order to bring the meter to the UK market, performing a rigorous testing and verification process at SMS’s dedicated test lab in Bolton, Lancashire.
SMS has so far installed 1.27 million domestic smart meters on behalf of energy suppliers as part of the smart meter rollout and has a total of 3.74 million metering and data assets under its management.
The majority of UK customers have not been able to take advantage of smart meters, which automatically log energy consumption to facilitate accurate billing. Smart meters are also an essential enabler of energy efficiency and green technologies – such as electric vehicles – that encourage flexible demand and help reduce carbon emissions and costs.
The development means that hundreds of thousands of customers connected to a three-phase supply across the domestic and I&C markets will now be able to join the UK’s energy revolution by having a smart meter installed.
As a second-generation smart meter (SMETS2) the new technology will allow customers – from homes and small businesses to organisations with larger and more complex electricity supplies – to connect to the secure nationwide network run by the Data Communications Company (Smart DCC), enabling seamless switching between energy suppliers. According to the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS), as of 31 March 2020 there were 21.5 million smart and advanced meters operating in homes and small business, of which Smart DCC has confirmed over 4.6 million of these meters are SMETS2.
Source: Smart Energy International

The Spanish ministry for ecological transition (MITECO) will allocate, over the next few months, EUR 316 million (USD 374.9m) to support renewables-based projects for the production of thermal and electrical energy.
The government said on Tuesday it will distribute EUR 246 million in aid for renewable energy projects through competitive calls. In addition to these, there will be specific calls for the Balearic and the Canary Islands, for EUR 20 million and EUR 54 million, respectively.
The government intends to allocate the money for green thermal projects, such as renewable gas or concentrating solar power (CSP), as well as wind or photovoltaic (PV) projects which may include storage systems.
The amount per project will be determined in each of the competitive processes. The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) will be a co-financier. Among the criteria for awarding winners, the government will take into consideration several points, including the location, job creation potential, rural development, the innovative nature of the projects and the type of end-use.
MITECO said this aid for renewables will also support the Just Transition in coal regions and the recovery after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Source: Renewables Now
Global Coal Fleet Shrank for First Time on Record in 2020
The world’s fleet of coal-fired power stations has got smaller for the first time on record, with more capacity retired in the first half of 2020 than the amount opened.
Please click here to read the full report.