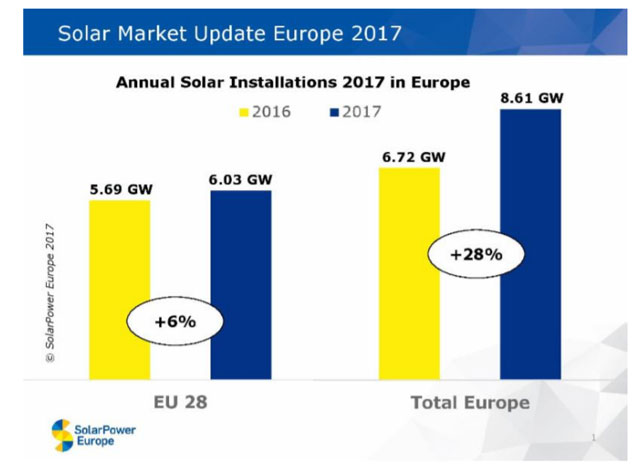
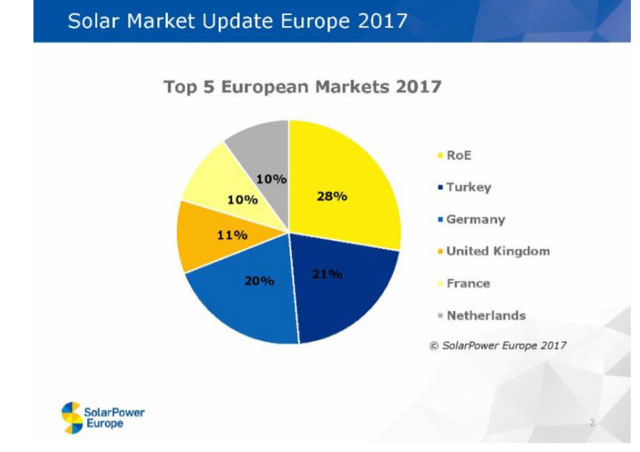
Occupational Health and Safety is put on the table in Antalya, Turkey 
"2nd Occupational Health and Safety Congress in Electricity Distribution Sector" organized by the Association of Electricity Distribution System Operators (ELDER) has started today. The congress, which takes place in Antalya on February 15-17, has been inaugurated by Deputy Undersecretary of Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources Abdullah Tancan, General Director of Turkish Electricity Distribution Corporation (TEDAŞ) Halil İbrahim Leventoğlu, Deputy General Director of Turkish Electricity Transmission Corporation (TEİAŞ) Orhan Kaldırım, President of Turkish Energy, Water and Gas Workers Union (TES-İŞ) Mustafa Şahin and ELDER Vice Chairman Yaşar Arslan.
While occupational accidents occurring in Turkey and all over the world were put on the table, developments and measures which could be taken were discussed in detail.
At 2nd Occupational Health and Safety Congress the theme of which is organized with "Prevention Culture" and under the sponsorship of SFE International, Hefe Enerji and Kermel; fundamental principles and applications of grounding, working at height in distribution sector, and the concept of "OHS culture", and the subject of 'How to create OHS culture?' were discussed.

Making the inaugural speech of the congress, Deputy Undersecretary of Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources Abdullah Tancan said: "If we figure out the reasons behind the occupational accidents, we can take the necessary measures. Today, two primary rates are used in occupational accident statistics in almost every country: accident incidence rate and accident severity rate... Accident incidence rate refers to the number of accidents occurring per million man/hours worked in a certain period and resulting in incapacity of employees for a period exceeding one day. Accident severity rate refers to the number of man-days lost due to occupational accidents per million man-hours worked in a certain period. Research conducted on occupational accidents reveal two primary reasons behind them. The first one is human-related reasons and the second one is physical and mechanical environment-related reasons... When we look at these reasons, we see that nearly 90% of them are human-related reasons and nearly 10% of them are physical and mechanical environment-related reasons. At this point, it is better to focus on human-related reasons. Each employee has her/his own personal, physiological and psychological characteristics, and each one of them is among the factors playing a role in accidents. When we look at the personal characteristics; we can group them as age, sex, marital status, status, seniority and educational level. Age remains one of the most critical factors taking into consideration the frequency of occupational accidents... According to Social Security Institution (SSI) data, the rate of occupational accidents among young employees is higher than those among older employees... The highest frequency rate is among employees aged 25–29, followed by employees aged 18-24. However, occupational accident rate among those aged 30-34 and above shows a notable falling tendency. Another subject to be discussed is sex... It is one of the most important factors playing a role in occupational accidents... The occupational accident rate among men is higher than those among women... Marital status remains another critical factor... According to data, the rate of occupational accidents among single employees is higher. On the other hand; the higher the status is, the less occupational accidents occur. Research conducted indicates that accident rate is the highest among employees who acquire from a day to a year of seniority. This rate is lower among employees who acquire from a year to two years of seniority. We see that accident rate is the lowest among those who have seniority of 5 years and more. Likewise, the higher the educational level is, the less occupational accidents happen. When we look at the physiological properties, we see that vision loss, hearing loss, physical incompatibility, incompatible body structure, sleep deprivation and fatigue are among these reasons. Last but not least psychological features: minimum mental incompetence, emotional structure, clumsiness, dissatisfaction, overconfidence, stress, lack of concentration on her/his work and environment, and negligence of employee with regard to her/his working area... When hiring employees, employers should subject them to psychological tests just like they subject them to physical tests. The reason is that the above-stated reasons are among the factors contributing to occupational accidents..."

"Electric power has an indisputable priority for people"
General Director of TEDAŞ Halil İbrahim Leventoğlu stated that, as distribution companies, they bear tremendous responsibilities for high quality service provision in electricity distribution sector, and added that "The most significant responsibilities are providing a safe environment where employees can work without worrying about their lives, identifying risk factors and taking the necessary actions, and realizing works which can protect physical and mental health against occupational accidents and occupational diseases. It is an obligation to act primarily with a human, health and occupational safety understanding and to create awareness among employees and employers in this direction." Mr. Leventoğlu touched on the significance of electricity in human life and added that: "High quality and continuous electricity is of high importance for quality living. I'd like to state that, as TEDAŞ, we begin works so as to change this picture. It is crucial to show a maximum effort so as to seek compliance with technical specifications prepared by our institution and with the relevant standards with a view to enhancing the quality of equipment used on the grounds that power failures cause occupational accidents.

Deputy General Director of TEİAŞ Orhan Kaldırım referred to the significance of adopting a proactive approach in occupational health and safety and said that: "Adopting a proactive approach in occupational health and safety means having a safety culture. Acquiring a safety culture means a superordinate goal which we always wish to achieve. We designated 2018 as education and occupational health and safety year in line with opinions of the Minister of Energy and Natural Resources Mr. Berat Albayrak. Within this scope, we put various projects into effect such as R&D works for virtual reality, theatrical education, OHS (Occupational Health and Safety) videos and uniform insulated fireproof suit. I am of the opinion that this congress will enrich us in terms of occupational health and safety."

In his speech, President of TES-İŞ Mustafa Şahin reminded a finding of International Labor Organization (ILO) on occupational accidents and added that: "ILO states that all occupational diseases and 98% of occupational accidents are preventable. As labor unions, we stand behind the underlying understanding of ILO's statement. We believe that, first of all, all segments in business life should adopt and promote this understanding of ILO so as to create a 'prevention and safety culture' in our country. The failure to create this culture and to develop preventive solutions at the desired level in Turkey is the most crucial reason behind our losses. We, all together, have to find a way to raise social consciousness and awareness, identify risks beforehand, establish a data collection and record system functioning smoothly, and, eventually, prevent accidents and diseases at source.

Hosting the congress on behalf of ELDER, ELDER Vice Chairman Yaşar Aslan stated that: "As ELDER, we undertake to create a sound occupational health and safety culture in all electricity distribution companies and to raise OHS consciousness in the sector so as to ensure that all employees making efforts for our sector work under the highest occupational safety measures. We, as ELDER, are organizing 2nd Occupational Health and Safety Congress in Electricity Distribution Sector within this scope."
Mr. Arslan pointed out the significance of occupational health and safety, touched on striking figures and added that: "Occupational health and safety subject is handled at United Nations level, and it is deemed as one of the most critical subjects and as an issue which is open for improvement in business life no matter which country you go to. According to data obtained from International Labor Organization (ILO); there are, on average, 300 million occupational accidents and 160 million work-related diseases all over the world every year while 3 million employees lose their lives due to occupational accidents or work-related diseases. 141 employees lost their lives only in January 2018 in Turkey. Despite all these casualties, 'Safety Culture Report' prepared by the International Labor Organizations shows that all occupational diseases and 98% of occupational accidents are preventable. Nearly 4-5% of this rate occur in electricity sector. We lose nearly 4% of world population every year due to accidents which can be prevented if we take the necessary actions and carry out the required works. According to the latest statistics from Social Security Institution; 286,000 insured employees had occupational accidents and, unfortunately, 2000 of them lost their lives in these accidents in Turkey in 2016.
Arslan: "It is possible to prevent occupational accidents in electricity distribution sector to a large extent"
Arslan emphasized that works on occupational health and safety in electricity distribution sector prevent occupational accidents to a large extent. Arslan added: "As you know, there are certain quality management systems which should be abided by. As per these quality management systems, all working groups were defined through work instructions and work directives and field works were standardized. Thus, occupational accidents can be prevented to a large extent. I'd like to express that ongoing professional competence personnel certification processes also contribute to prevention of these accidents."
Nearly 300 participants attended the congress which aims to improve management systems in terms of occupational health and safety in business world and in institutions and contribute to the development of safety standards for electric power of workplaces.