Electricity Distribution Services Association - ELDER 13th Sector Meeting was held on a digital platform.
Fatih Donmez, Energy and Natural Resources Minister, Mustafa Elitas, The Grand National Assembly of Turkey (GNAT) Industry, Trade, Energy, Natural Resources, Information and Technology Commission President, Mustafa Yilmaz Energy Market Regulatory Authority (EMRA) President and Serhat Cecen, ELDER Board Chairman made the opening speeches of the meeting. Donmez, stated that an investment of $9.3 billion (66.7 billion Turkish liras) in total is planned for the fourth implementation period of 2021-2025 in the electricity distribution sector.
“This amount is approximately twice the investment budget of the previous implementation period. With new investments, we expanded the existing network every year,” he said. “In the Third Implementation Period of 2016-2020, our electricity distribution sector made an investment of 40 billion Turkish liras, exceeding the planned investment of 34 billion Turkish liras. Thus, an investment of 6 billion Turkish liras more than the planned investment amount was made.”
Donmez also said the planned investment includes $1.5 billion in expenditure for scheduled maintenance between 2021 and 2025.
"Developing Renewable Resources is Our Priority"
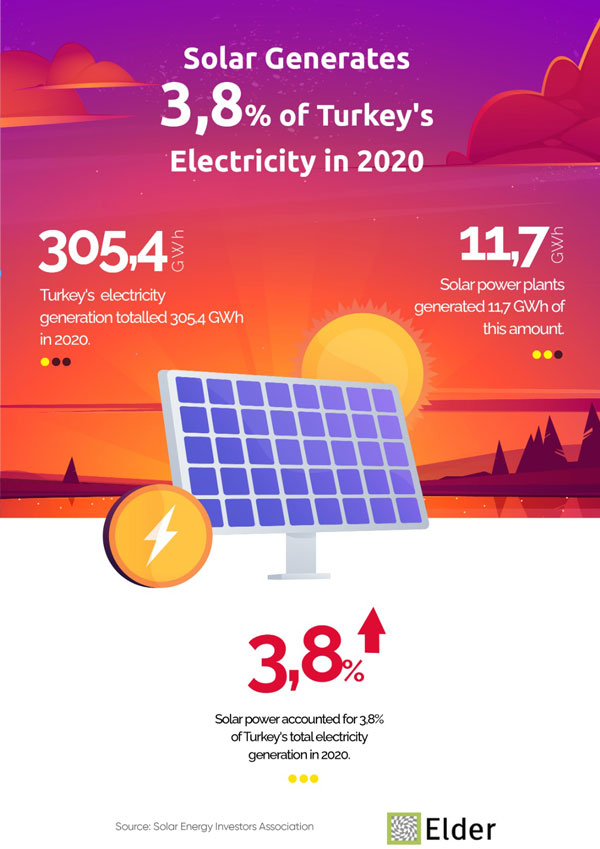
Mustafa Elitas, The Grand National Assembly of Turkey (GNAT) Industry, Trade, Energy, Natural Resources, Information and Technology Commission President emphasized that there is a decrease in electricity demand worldwide due to the pandemic. Elitas said, “Our priority is especially the development of renewable energy resources. Turkey has so far taken commissioning of solar power plants in 2014, the increase in the installed capacity of solar 9th country in the world, and 3rd position in Europe.
1 Billion TL has been Allowed for R&D
Mustafa Yilmaz, EMRA Chairman said that the great importance of the power outages from planned maintenance activities in order to bring Turkey's agenda. Yilmaz said, “Another important point is that planned maintenance activities are arranged through tariffs. As an institution, we have foreseen an annual budget of approximately 2.2 billion Turkish liras for planned maintenance expenditures”
"Uninterrupted Energy Supply During Pandemic”
Serhat Cecen, Chairman of the Board of ELDER, pointed out that the pandemic has been a part of life for a long time. In the pandemic period, he thanked the sector employees for making uninterrupted and continuous energy supply possible without avoiding any sacrifice.
"Investment Close to 67 Billion TL in the New Implementation Period"
He stated that they made an investment of 37 billion Turkish liras over the investment ceiling of 32.7 billion Turkish liras in the third implementation period, and in the 4th Implementation Period covering the years 2021-2025, it doubled the investment ceiling of the sector to 66.7 billion Turkish liras.
"Focus on Digitalization, R&D and Technology will be Improved"
Stating that they will focus on R&D and technology developments together with digitalization as the sector, he said, “We see the expansion of our digital service range as the most important supporter of consumer satisfaction and efficient operation structure.

Turkey's electricity production increased by 4.3% in December 2020 compared to the same month of 2019, as production in the country's industrial sector and consumption in agricultural irrigation rose, according to the latest data reported by the country's energy watchdog.
Total electricity production rose to approximately 26.8 million MegaWatt-hours (MWh), from 25.7 million MWh in December 2019, Turkey's Energy Market Regulatory Authority (EMRA) announced in its electricity market report for December 2020.
Turkey produced its electricity from several sources: 33.3% from natural gas, 22.4% from import coal, 14.8% from hydropower and 13.5% from lignite. Wind, geothermal, biomass, hard coal, asphaltite, solar power and fuel oil generated the remaining share.
Industrial sector consumption held the largest share at 44.1%, followed by the residential sector at 25.6%. The commercial sector ranked third with 22.7%, while agricultural irrigation and street lighting accounted for the remainder.
Turkey's installed electricity capacity was up 4.8% in December 2020 from the same period of 2019. Natural gas power plants comprised 28.8%, while 25.7% came from hydropower plants and 11.4% from lignite power plants. Imported coal, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass, hard coal, solar power, asphaltite, fuel oil, naphtha, LNG and diesel also contributed to installed capacity.
Source: Anadolu Agency

Europe’s biggest wind power generator Iberdrola pledged on Wednesday to invest 150 billion euros ($182.39 billion) on tripling its renewable capacity and doubling its network assets by 2030, bolstered by a rise in annual net profit.
Years of investment in low-emission generation and power grids have put the Spanish group squarely on investors’ radars as a beneficiary of an accelerating global pivot towards running economies on renewably sourced electricity.
It plans to operate 95 GigaWatts (GW) of clean power capacity by 2030. By comparison, the International Energy Agency estimated global renewable capacity hit 200 GW in 2020.
The investment plan builds on a pledge made last November to spend 75 billion euros between 2020 and 2025.
The extended spending spree is set to take the value of the network assets that churn out around half the company’s core earnings to 60 billion euros by the end of this decade.
Net profit rose 4.2% to 3.61 billion euros in 2020, meeting an average forecast of 3.60 billion euros drawn from eleven analysts polled by the company.
Growth in Brazil, the United Kingdom and Mexico balanced out a drop in Spain, where electricity demand shrank due to the coronavirus pandemic. Two thirds of the group’s core earnings are now generated outside Spain. Iberdrola’s shares dropped slightly at the market open then rose as much as 0.9%, to trade just over 3% lower than at the same time last year. Their value has more than doubled in the past five years, outstripping a 30% rise for European utilities collectively.
Source: Reuters

The penetration of smart electricity meters in North America reached 68% in 2020, according to a new study released by research firm Berg Insight. The research firm predicts that the installed base of smart electricity meters will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% between 2019 and 2025 to reach a total of 153.8 million units.
Over the next five years, the penetration of smart meters in the US will grow to reach a level of 84%, while the respective figure for the more advanced Canadian market will reach 92%.
Yearly shipments of smart electricity meters in North America is expected to grow from 9.8 million units in 2019 to 17.4 million units in 2025.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on deployments during 2020 with a year-over-year decrease of around 13% in annual shipment volumes.
The market is however expected to recover in 2021 with forecasted shipment volumes of 10.7 million units.
Along with the increase in smart meter refreshment projects, the development of smart metering technology in the North American market has in the last couple of years shifted focus to serving the demand of utilities which are to begin second-wave smart meter rollouts.
These utilities are now looking to leverage their existing network canopies for a wider array of smart city applications beyond metering, while also trying to figure out how to cope with the integration of the rapidly increasing number of electric vehicles and distributed energy resources into the grid infrastructure.
Source: Smart Energy International

Wind energy provided 16.4% of EU and UK power in 2020, bringing the industry closer to its objective of producing 50% of the bloc’s total electricity by 2050. But permitting issues, lockdowns and changing regulations threaten to slow down further deployment, the industry warns.
Denmark saw almost half of its electricity provided by wind in 2020, while Ireland saw 40% and Germany and the UK each had 27%. But even though 14.7 GW came online in 2020, last year saw a drop in installations, including a 22% fall in onshore wind as delays in the supply chain and lockdowns hampered progress.
The Netherlands installed the most wind capacity, with Germany coming in second. There are also new movers, like Poland, which saw significant growth from 53 MW in 2019 as most of the 1 GW auctioned in 2018 came online. Russia was also among the rising stars, with 0.8 GW commissioned. “This year there was much more diversification than in previous years. You see some newer faces in the top five,” said Ivan Komusanac, an analyst at trade association WindEurope.
There is currently around 220 GW of wind capacity in Europe, with Germany far out in front. New players include Sweden and Turkey, which are beginning to build up fleets, and Poland, which is expected to increase its capacity in the latter half of the decade. But Komusanac warned that EU countries are still not ambitious enough to meet the Commission’s current target for renewable energy by 2030, let alone the expected increase to meet the new climate target.
He said that countries would need to be installing 18 GW every year, but that current plans fall at least 3 GW short of this. In its current scenarios, WindEurope expects 105 GW to be installed in the next five years but warns this could be as low as 79 GW if COVID restrictions, permitting issues and delays in building up the grid continue.
“We also need to make sure governments do their work on permitting. If you want to reach the -55% target there will be much more need for offshore wind,” said Komusanac.
He added that recovery funding is absolutely crucial for the wind industry and needs to be used for building up grids and infrastructure, including ports and roads for offshore energy.
Source: Euractiv

If the future of cars is to be electric, the 2020s will be the decade that turns the tide.
Last year, demand for electric vehicles (EVs) led to a meteoric rise in Tesla’s stock price, turning the electric vehicle pioneer from a bankruptcy candidate into the most valuable car manufacturer in the world. Domestically, over 18 million electric vehicles are expected to hit the road over the next 10 years, boosted by a notably pro-electric Biden administration.
Some may look at this growth in EVs as a missed investment opportunity. However, for those in commercial real estate, the true opportunity has just begun: the race for charging stations. While America now has 1.6 million electric vehicles, public charging stations have seriously lagged behind—only 40,000 have been registered with the U.S. Department of Energy.
This is a fraction compared to the roughly 150,000 gas stations in the U.S—and even a steeper fraction compared to the ambitious 500,000 charging stations target set by the Biden administration. This has led to pent up demand and charging infrastructure investments are already expected to exceed $13 billion over the next 5 years.
Why does this matter to commercial real estate managers? Because while charging stations ostensibly deliver power to electric vehicles, they also deliver customers to retail locations.
In other words, drivers waiting to recharge their vehicles are now captive, on-location customers—precisely what physical shopping centers have struggled to attract. The concept of up-selling drivers during refueling stops has been a tool of the convenience store industry for decades. Currently, 82% of gas stations have on-site convenience stores, generating $250 billion in revenues.
Source: Forbes
Connecting the Dots: Distribution Grid İnvestment to Power the Energy Transition
Europe’s distribution grids are the backbone of the digital and energy transition. They connect the dots by integrating the majority of renewables, enabling the creation of new services for consumers, and ensuring a reliable electricity flow. €375-425 billion of investments are needed to make them fit-for-purpose in an increasingly decarbonised, decentralised and digitalised power system.
Please click here to read the full report.
Solarex Istanbul
01 - 03 April 2021
8th International Istanbul Smart Grids and Cities Congress and Expo (ICSG 2021)
04 - 05 June 2021
2021 IEEE PES Futuring the Power Grid
14 - 17 September 2021
11. Turkey Energy Summit
10 - 12 October 2021
14. EIF World Energy Congress and Expo
13 - 15 October 2021 / Antalya
European Utility Week (Enlit Europe)
30 November - 2 December 2021